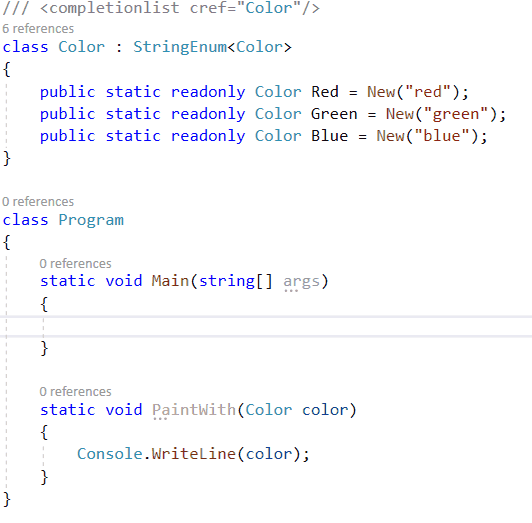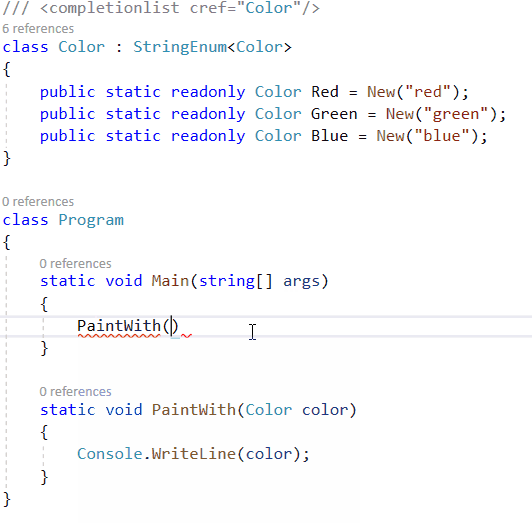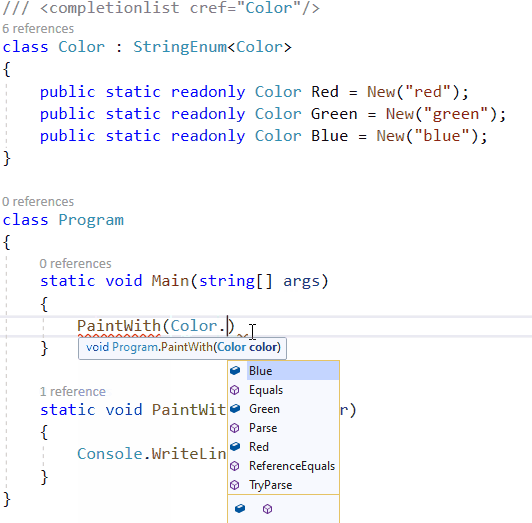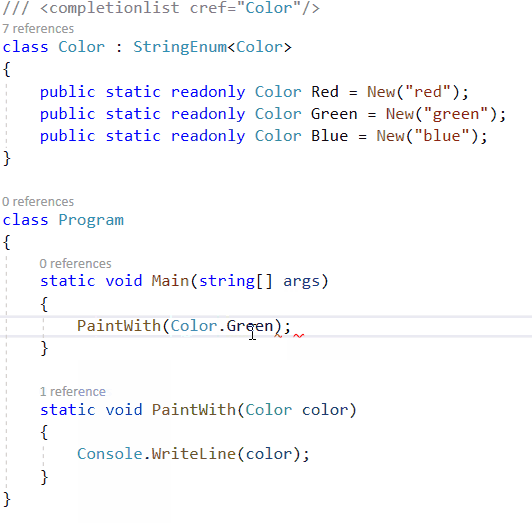
对于较大的字符串枚举集,列出的示例可能会令人厌烦。如果需要状态代码列表或其他基于字符串的枚举列表,则使用属性系统很烦人,而带有自身实例的静态类则很烦人。对于我自己的解决方案,我使用T4模板来简化具有字符串支持的枚举的过程。结果类似于HttpMethod类的工作原理。
您可以像这样使用它:
string statusCode = ResponseStatusCode.SUCCESS; // Automatically converts to string when needed
ResponseStatusCode codeByValueOf = ResponseStatusCode.ValueOf(statusCode); // Returns null if not found
// Implements TypeConverter so you can use it with string conversion methods.
var converter = System.ComponentModel.TypeDescriptor.GetConverter(typeof(ResponseStatusCode));
ResponseStatusCode code = (ResponseStatusCode) converter.ConvertFromInvariantString(statusCode);
// You can get a full list of the values
bool canIterateOverValues = ResponseStatusCode.Values.Any();
// Comparisons are by value of the "Name" property. Not by memory pointer location.
bool implementsByValueEqualsEqualsOperator = "SUCCESS" == ResponseStatusCode.SUCCESS;
您从一个Enum.tt文件开始。
<#@ include file="StringEnum.ttinclude" #>
<#+
public static class Configuration
{
public static readonly string Namespace = "YourName.Space";
public static readonly string EnumName = "ResponseStatusCode";
public static readonly bool IncludeComments = true;
public static readonly object Nodes = new
{
SUCCESS = "The response was successful.",
NON_SUCCESS = "The request was not successful.",
RESOURCE_IS_DISCONTINUED = "The resource requested has been discontinued and can no longer be accessed."
};
}
#>
然后,添加您的StringEnum.ttinclude文件。
<#@ template debug="false" hostspecific="false" language="C#" #>
<#@ assembly name="System.Core" #>
<#@ import namespace="System" #>
<#@ import namespace="System.Linq" #>
<#@ import namespace="System.Text" #>
<#@ import namespace="System.Reflection" #>
<#@ import namespace="System.Collections.Generic" #>
<#@ output extension=".cs" #>
<#@ CleanupBehavior processor="T4VSHost" CleanupAfterProcessingtemplate="true" #>
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// <auto-generated>
// This code was generated by a tool.
//
// Changes to this file may cause incorrect behavior and will be lost if
// the code is regenerated.
// </auto-generated>
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Globalization;
namespace <#= Configuration.Namespace #>
{
/// <summary>
/// TypeConverter implementations allow you to use features like string.ToNullable(T).
/// </summary>
public class <#= Configuration.EnumName #>TypeConverter : TypeConverter
{
public override bool CanConvertFrom(ITypeDescriptorContext context, Type sourceType)
{
return sourceType == typeof(string) || base.CanConvertFrom(context, sourceType);
}
public override object ConvertFrom(ITypeDescriptorContext context, CultureInfo culture, object value)
{
var casted = value as string;
if (casted != null)
{
var result = <#= Configuration.EnumName #>.ValueOf(casted);
if (result != null)
{
return result;
}
}
return base.ConvertFrom(context, culture, value);
}
public override object ConvertTo(ITypeDescriptorContext context, CultureInfo culture, object value, Type destinationType)
{
var casted = value as <#= Configuration.EnumName #>;
if (casted != null && destinationType == typeof(string))
{
return casted.ToString();
}
return base.ConvertTo(context, culture, value, destinationType);
}
}
[TypeConverter(typeof(<#= Configuration.EnumName #>TypeConverter))]
public class <#= Configuration.EnumName #> : IEquatable<<#= Configuration.EnumName #>>
{
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// V A L U E S _ L I S T
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
<# Write(Helpers.PrintEnumProperties(Configuration.Nodes)); #>
private static List<<#= Configuration.EnumName #>> _list { get; set; } = null;
public static List<<#= Configuration.EnumName #>> ToList()
{
if (_list == null)
{
_list = typeof(<#= Configuration.EnumName #>).GetFields().Where(x => x.IsStatic && x.IsPublic && x.FieldType == typeof(<#= Configuration.EnumName #>))
.Select(x => x.GetValue(null)).OfType<<#= Configuration.EnumName #>>().ToList();
}
return _list;
}
public static List<<#= Configuration.EnumName #>> Values()
{
return ToList();
}
/// <summary>
/// Returns the enum value based on the matching Name of the enum. Case-insensitive search.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static <#= Configuration.EnumName #> ValueOf(string key)
{
return ToList().FirstOrDefault(x => string.Compare(x.Name, key, true) == 0);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// I N S T A N C E _ D E F I N I T I O N
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public string Name { get; private set; }
public string Description { get; private set; }
public override string ToString() { return this.Name; }
/// <summary>
/// Implcitly converts to string.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="d"></param>
public static implicit operator string(<#= Configuration.EnumName #> d)
{
return d.ToString();
}
/// <summary>
/// Compares based on the == method. Handles nulls gracefully.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a"></param>
/// <param name="b"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static bool operator !=(<#= Configuration.EnumName #> a, <#= Configuration.EnumName #> b)
{
return !(a == b);
}
/// <summary>
/// Compares based on the .Equals method. Handles nulls gracefully.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a"></param>
/// <param name="b"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static bool operator ==(<#= Configuration.EnumName #> a, <#= Configuration.EnumName #> b)
{
return a?.ToString() == b?.ToString();
}
/// <summary>
/// Compares based on the .ToString() method
/// </summary>
/// <param name="o"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public override bool Equals(object o)
{
return this.ToString() == o?.ToString();
}
/// <summary>
/// Compares based on the .ToString() method
/// </summary>
/// <param name="other"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool Equals(<#= Configuration.EnumName #> other)
{
return this.ToString() == other?.ToString();
}
/// <summary>
/// Compares based on the .Name property
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public override int GetHashCode()
{
return this.Name.GetHashCode();
}
}
}
<#+
public static class Helpers
{
public static string PrintEnumProperties(object nodes)
{
string o = "";
Type nodesTp = Configuration.Nodes.GetType();
PropertyInfo[] props = nodesTp.GetProperties().OrderBy(p => p.Name).ToArray();
for(int i = 0; i < props.Length; i++)
{
var prop = props[i];
if (Configuration.IncludeComments)
{
o += "\r\n\r\n";
o += "\r\n ///<summary>";
o += "\r\n /// "+Helpers.PrintPropertyValue(prop, Configuration.Nodes);
o += "\r\n ///</summary>";
}
o += "\r\n public static readonly "+Configuration.EnumName+" "+prop.Name+ " = new "+Configuration.EnumName+"(){ Name = \""+prop.Name+"\", Description = "+Helpers.PrintPropertyValue(prop, Configuration.Nodes)+ "};";
}
o += "\r\n\r\n";
return o;
}
private static Dictionary<string, string> GetValuesMap()
{
Type nodesTp = Configuration.Nodes.GetType();
PropertyInfo[] props= nodesTp.GetProperties();
var dic = new Dictionary<string,string>();
for(int i = 0; i < props.Length; i++)
{
var prop = nodesTp.GetProperties()[i];
dic[prop.Name] = prop.GetValue(Configuration.Nodes).ToString();
}
return dic;
}
public static string PrintMasterValuesMap(object nodes)
{
Type nodesTp = Configuration.Nodes.GetType();
PropertyInfo[] props= nodesTp.GetProperties();
string o = " private static readonly Dictionary<string, string> ValuesMap = new Dictionary<string, string>()\r\n {";
for(int i = 0; i < props.Length; i++)
{
var prop = nodesTp.GetProperties()[i];
o += "\r\n { \""+prop.Name+"\", "+(Helpers.PrintPropertyValue(prop,Configuration.Nodes)+" },");
}
o += ("\r\n };\r\n");
return o;
}
public static string PrintPropertyValue(PropertyInfo prop, object objInstance)
{
switch(prop.PropertyType.ToString()){
case "System.Double":
return prop.GetValue(objInstance).ToString()+"D";
case "System.Float":
return prop.GetValue(objInstance).ToString()+"F";
case "System.Decimal":
return prop.GetValue(objInstance).ToString()+"M";
case "System.Long":
return prop.GetValue(objInstance).ToString()+"L";
case "System.Boolean":
case "System.Int16":
case "System.Int32":
return prop.GetValue(objInstance).ToString().ToLowerInvariant();
case "System.String":
return "\""+prop.GetValue(objInstance)+"\"";
}
return prop.GetValue(objInstance).ToString();
}
public static string _ (int numSpaces)
{
string o = "";
for(int i = 0; i < numSpaces; i++){
o += " ";
}
return o;
}
}
#>
最后,重新编译Enum.tt文件,输出如下所示:
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// <auto-generated>
// This code was generated by a tool.
//
// Changes to this file may cause incorrect behavior and will be lost if
// the code is regenerated.
// </auto-generated>
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace YourName.Space
{
public class ResponseStatusCode
{
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// V A L U E S _ L I S T
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
///<summary>
/// "The response was successful."
///</summary>
public static readonly ResponseStatusCode SUCCESS = new ResponseStatusCode(){ Name = "SUCCESS", Description = "The response was successful."};
///<summary>
/// "The request was not successful."
///</summary>
public static readonly ResponseStatusCode NON_SUCCESS = new ResponseStatusCode(){ Name = "NON_SUCCESS", Description = "The request was not successful."};
///<summary>
/// "The resource requested has been discontinued and can no longer be accessed."
///</summary>
public static readonly ResponseStatusCode RESOURCE_IS_DISCONTINUED = new ResponseStatusCode(){ Name = "RESOURCE_IS_DISCONTINUED", Description = "The resource requested has been discontinued and can no longer be accessed."};
private static List<ResponseStatusCode> _list { get; set; } = null;
public static List<ResponseStatusCode> ToList()
{
if (_list == null)
{
_list = typeof(ResponseStatusCode).GetFields().Where(x => x.IsStatic && x.IsPublic && x.FieldType == typeof(ResponseStatusCode))
.Select(x => x.GetValue(null)).OfType<ResponseStatusCode>().ToList();
}
return _list;
}
public static List<ResponseStatusCode> Values()
{
return ToList();
}
/// <summary>
/// Returns the enum value based on the matching Name of the enum. Case-insensitive search.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static ResponseStatusCode ValueOf(string key)
{
return ToList().FirstOrDefault(x => string.Compare(x.Name, key, true) == 0);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// I N S T A N C E _ D E F I N I T I O N
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public override string ToString() { return this.Name; }
/// <summary>
/// Implcitly converts to string.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="d"></param>
public static implicit operator string(ResponseStatusCode d)
{
return d.ToString();
}
/// <summary>
/// Compares based on the == method. Handles nulls gracefully.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a"></param>
/// <param name="b"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static bool operator !=(ResponseStatusCode a, ResponseStatusCode b)
{
return !(a == b);
}
/// <summary>
/// Compares based on the .Equals method. Handles nulls gracefully.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a"></param>
/// <param name="b"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static bool operator ==(ResponseStatusCode a, ResponseStatusCode b)
{
return a?.ToString() == b?.ToString();
}
/// <summary>
/// Compares based on the .ToString() method
/// </summary>
/// <param name="o"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public override bool Equals(object o)
{
return this.ToString() == o?.ToString();
}
/// <summary>
/// Compares based on the .Name property
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public override int GetHashCode()
{
return this.Name.GetHashCode();
}
}
}