如何跟踪广度优先搜索的路径,如以下示例所示:
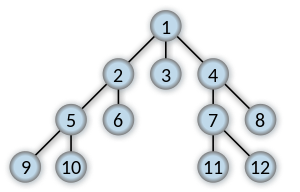
如果搜索key 11,则返回连接1到11 的最短列表。
[1, 4, 7, 11]如何跟踪广度优先搜索的路径,如以下示例所示:

如果搜索key 11,则返回连接1到11 的最短列表。
[1, 4, 7, 11]Answers:
您应该先查看http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Breadth-first_search。
下面是一个快速实现,其中我使用列表列表表示路径队列。
# graph is in adjacent list representation
graph = {
'1': ['2', '3', '4'],
'2': ['5', '6'],
'5': ['9', '10'],
'4': ['7', '8'],
'7': ['11', '12']
}
def bfs(graph, start, end):
# maintain a queue of paths
queue = []
# push the first path into the queue
queue.append([start])
while queue:
# get the first path from the queue
path = queue.pop(0)
# get the last node from the path
node = path[-1]
# path found
if node == end:
return path
# enumerate all adjacent nodes, construct a new path and push it into the queue
for adjacent in graph.get(node, []):
new_path = list(path)
new_path.append(adjacent)
queue.append(new_path)
print bfs(graph, '1', '11')另一种方法是维护从每个节点到其父节点的映射,并在检查相邻节点时记录其父节点。搜索完成后,只需根据父映射进行回溯即可。
graph = {
'1': ['2', '3', '4'],
'2': ['5', '6'],
'5': ['9', '10'],
'4': ['7', '8'],
'7': ['11', '12']
}
def backtrace(parent, start, end):
path = [end]
while path[-1] != start:
path.append(parent[path[-1]])
path.reverse()
return path
def bfs(graph, start, end):
parent = {}
queue = []
queue.append(start)
while queue:
node = queue.pop(0)
if node == end:
return backtrace(parent, start, end)
for adjacent in graph.get(node, []):
if node not in queue :
parent[adjacent] = node # <<<<< record its parent
queue.append(adjacent)
print bfs(graph, '1', '11')上面的代码基于没有循环的假设。
我非常喜欢qiao的第一个答案!这里唯一缺少的是将顶点标记为已访问。
为什么我们需要这样做?
让我们想象一下,从节点11连接了另一个节点号13。现在我们的目标是找到节点13。
经过一点点运行,队列将如下所示:
[[1, 2, 6], [1, 3, 10], [1, 4, 7], [1, 4, 8], [1, 2, 5, 9], [1, 2, 5, 10]]请注意,最后有两个路径的节点编号为10。
这意味着从节点号10开始的路径将被检查两次。在这种情况下,它看起来并不那么糟糕,因为10号节点没有任何子节点。但是,这可能真的很糟糕(即使在这里我们也会无故检查两次该节点。)
13号节点不在其中这些路径,因此程序在到达最后一个节点号为10的第二条路径之前不会返回。我们将对其进行重新检查。
我们所缺少的只是一个标记访问的节点而不要再次检查它们的集合。
这是修改后的qiao的代码:
graph = {
1: [2, 3, 4],
2: [5, 6],
3: [10],
4: [7, 8],
5: [9, 10],
7: [11, 12],
11: [13]
}
def bfs(graph_to_search, start, end):
queue = [[start]]
visited = set()
while queue:
# Gets the first path in the queue
path = queue.pop(0)
# Gets the last node in the path
vertex = path[-1]
# Checks if we got to the end
if vertex == end:
return path
# We check if the current node is already in the visited nodes set in order not to recheck it
elif vertex not in visited:
# enumerate all adjacent nodes, construct a new path and push it into the queue
for current_neighbour in graph_to_search.get(vertex, []):
new_path = list(path)
new_path.append(current_neighbour)
queue.append(new_path)
# Mark the vertex as visited
visited.add(vertex)
print bfs(graph, 1, 13)该程序的输出将是:
[1, 4, 7, 11, 13]没有轻松的检查。
collections.deque的queue作为list.pop(0)招致O(n)内存走势。同样,为了后代的缘故,如果您想进行DFS设置,则path = queue.pop()在这种情况下,变量queue实际上就像a一样stack。
非常简单的代码。每次发现节点时,您都会追加路径。
graph = {
'A': set(['B', 'C']),
'B': set(['A', 'D', 'E']),
'C': set(['A', 'F']),
'D': set(['B']),
'E': set(['B', 'F']),
'F': set(['C', 'E'])
}
def retunShortestPath(graph, start, end):
queue = [(start,[start])]
visited = set()
while queue:
vertex, path = queue.pop(0)
visited.add(vertex)
for node in graph[vertex]:
if node == end:
return path + [end]
else:
if node not in visited:
visited.add(node)
queue.append((node, path + [node]))我以为我会尝试将此代码编写起来很有趣:
graph = {
'1': ['2', '3', '4'],
'2': ['5', '6'],
'5': ['9', '10'],
'4': ['7', '8'],
'7': ['11', '12']
}
def bfs(graph, forefront, end):
# assumes no cycles
next_forefront = [(node, path + ',' + node) for i, path in forefront if i in graph for node in graph[i]]
for node,path in next_forefront:
if node==end:
return path
else:
return bfs(graph,next_forefront,end)
print bfs(graph,[('1','1')],'11')
# >>>
# 1, 4, 7, 11如果需要循环,可以添加以下内容:
for i, j in for_front: # allow cycles, add this code
if i in graph:
del graph[i]我既喜欢@乔的第一个答案,又喜欢@Or的加法。为了减少处理量,我想补充一下Or的答案。
在@Or的答案中,访问节点的跟踪很棒。我们还可以允许程序比当前状态早退出。在for循环的某个点上,current_neighbour必须是end,一旦发生,就会找到最短路径,程序可以返回。
我将修改方法如下,请密切注意for循环
graph = {
1: [2, 3, 4],
2: [5, 6],
3: [10],
4: [7, 8],
5: [9, 10],
7: [11, 12],
11: [13]
}
def bfs(graph_to_search, start, end):
queue = [[start]]
visited = set()
while queue:
# Gets the first path in the queue
path = queue.pop(0)
# Gets the last node in the path
vertex = path[-1]
# Checks if we got to the end
if vertex == end:
return path
# We check if the current node is already in the visited nodes set in order not to recheck it
elif vertex not in visited:
# enumerate all adjacent nodes, construct a new path and push it into the queue
for current_neighbour in graph_to_search.get(vertex, []):
new_path = list(path)
new_path.append(current_neighbour)
queue.append(new_path)
#No need to visit other neighbour. Return at once
if current_neighbour == end
return new_path;
# Mark the vertex as visited
visited.add(vertex)
print bfs(graph, 1, 13)输出和其他所有内容都将相同。但是,该代码将花费更少的时间来处理。这在较大的图上特别有用。我希望这对以后的人有所帮助。